This
chapter has been excerpted from book "Essential Windows Communication
Foundation (WCF): For .NET Framework" with permission from
Addison-Wesley"
The
new Web programming capabilities in WCF simplify the building of
services for use on the Web. This chapter covers these services,
including SOAP, POX, the UriTemplate class, the webHttpBinding binding,
configuration-free hosting, and content syndication models.
PROGRAMMABLE
WEB REFERS to a set of enabling technologies designed to help
developers build the services for the Web. There are many ways of
building services for the Web. We have already mentioned throughout the
book how WCF can be used to build WS-* Web services, which use SOAP,
HTTP, and XML. Services based on WS-* are typically built using a
service-oriented architecture approach.
A service-oriented architecture approach follows four main tenants:
- Boundaries are explicit.
- Services are autonomous.
- Services share schema and contract, no class.
- Services compatibility is determined based on policy (see http://msdn.microsoft.com/msdnmag/issues/04/01/Indigo/default.aspx).
Services
can be built from other styles of architectures, such as
Representational State Transfer (REST). REST is an architectural style
described in a dissertation from Roy Fielding (see www.ics.uci.edu/~fielding/pubs/dissertation/rest_arch_style.htm). REST follows a set of principles that are based on constraints:
- A client/server approach is used to separate user interface from data storage.
- Client/server interaction is stateless.
- Network efficiency is improved using caching.
- Components of the system interact using a uniform interface.
- The overall system can be composed using a layering approach.
The
REST architectural style is often referred to as the architectural
style of the Web because the constraints can easily be seen in modern
Web architectures. We mention service orientation and REST because these
are two common architectural styles for building services on the Web
today. It is important to understand that WCF does not dictate the
architectural style or manner in which to build services. Instead it
exposes a set of features and capabilities that allow you to build
services using a variety of architectural styles. The rest of this
chapter will focus on the features that help developers build services
for the Web. To help understand the motivation behind these new
features, we will examine how developers use the Web today.
All About the URI
Most
everyone should be familiar with URIs because this is how people browse
the Web today. People access resources, such as HTML pages, via URIs
typed into the address bar of their browsers. Browsers can access a
variety of resources using URIs, including images, videos, data,
applications, and more. Accessing of resources via a URI is also one of
the principles behind the REST architectural style.
Table 13.1 shows several examples of resources on the Web that can be accessed in this manner.
Table 13.1. URI Examples
| URI | Description |
| http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes?s=MSFT&f=spt1d | Microsoft (MSFT) stock quotes in comma-separated (CSV) format from Yahoo! |
| http://finance.google.com/finance/info?q=MSFT | Microsoft (MSFT) stock quote in custom JSON format from Google |
| http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple | A Wikipedia Web page about "Apples" |
| www.weather.com/weather/local/02451 | Weather information for Waltham, MA from Weather.com |
| www.msnbc.msn.com/id/20265063/ | News article on MSN.com |
| http://pipes.yahoo.com/pipes/pipe.run?_id=jlM12Ljj2xGAdeUR1vC6Jw& _render=json&merger=eg | Wall Street corporate events listing services (for example, stock splits, mergers, and so on) in JSON format |
| http://rss.slashdot.org/Slashdot/slashdot | Slashdot syndication feed in RSS format |
| http://api.flickr.com/services/rest/?method=flickr.photos.search& api_key=20701ea0647b482bcb124b1c80db976f&text=stocks | Flickr photo search in custom XML format |
http://finance.google.com/finance/info?q=MSFT
What
is not represented is whether this URL is accessed using an HTTP GET or
some other HTTP action. For now, we will assume that GET is being used.
The URL can be rewritten with a parameter for the stock symbol in place
of the MSFT stock symbol. Using this simplification of the URL, we can
identify a number of resources.http://finance.google.com/finance/info?q={StockSymbol}
This example helps form the basis for how we can identify and access resources on the Web.The Ubiquitous GET
One thing in common with all the URIs in Table 13.1 is that they use the HTTP protocol to access resources. The HTTP protocol is considered the protocol of the Web. The original purpose of HTTP was to exchange HTML pages, but it has since been used to access all types of resources, including images, video, applications, and much more. The way in which it does this is by specifying a resource identifier and an action to be performed on that resource. URIs identify the resource. The action is defined by a set of HTTP verbs that specify the action to be performed on the resource. Table 13.2 shows a list of common HTTP verbs used on the Web today. There are many ways to interact with resources over the Web using the HTTP protocol, but none is as ubiquitous as GET. GET is by far the most widely used verb. POST comes in second, followed by other verbs such as PUT and DELETE.Table 13.2. Common HTTP Verbs
| Verb | Description |
| GET | Retrieve the resource identified by the URI. |
| POST | Send a resource to the server based on the resource identified by the URI. |
| PUT | Store a resource based on the resource identified by the URI. |
| DELETE | Delete a resource based on the resource identified by the URI. |
| HEAD | Identical to GET except that the response is not returned. This is used to retrieve metadata for the resource identified by the URI. |
Format Matters
The list of URIs in Table 13.1 demonstrates the vast number of formats available on the Web today. The content returned from these URIs includes HTML, XML, JSON, RSS, CSV, and custom formats. This means that developers have not found a single format that can represent all resources on the Web. For a while, it seemed that all roads would lead to XML as the single format. XML is a great mechanism for providing structure to data and for sharing information. For example, SOAP is a protocol for exchanging XML-based messages and is the foundation for traditional Web services. WCF provides support for the SOAP protocol. SOAP does more than provide structure to data, though. SOAP adds header information, which allows for advanced capabilities such as transport independence, message-level security, and transactions. Web developers are not necessarily concerned about such capabilities and need a way to exchange information. In these situations, formats such as Plain-Old-XML (POX) and JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) are often used.POX is usually about developers not needing the capabilities that WS-* has to offer and not wanting the perceived overhead of SOAP. In these situations, using POX is a "good enough" format for their needs. JSON, on the other hand, is an efficient format for returning data to browser clients that leverage JavaScript. JSON as a format is more efficient than SOAP and can offer significant performance and scalability benefits when you are trying to reduce the number of bytes on the wires. What this comes down to is that format matters, and developers need to be able to work with a number of formats when using the Web.
Web Programming with WCF
Table 13.3 highlights some of the major features available to developers when they use WCF and .NET Framework 3.5. The remainder of this chapter focuses on the features within WCF that help enable the "programmable Web."Table 13.3. Web Programming Features in .NET Framework 3.5
| Verb | Description |
| Uri and UriTemplates | Enhanced support for working with URIs to support REST architectural patterns. |
| webHttpBinding Binding | A new binding that builds in support for POX and JSON, formal support for HTTP verbs including GET, and URI-based dispatching. |
| ASP.NET AJAX Integration | Integration with ASP.NET AJAX to support client-side service proxies. |
| Content Syndication | Classes for publishing and consuming RSS and ATOM syndication feeds. |
URI and UriTemplates
Microsoft
has provided support for URIs since .NET Framework v1.0. The System.Uri
class allows developers to define and parse basic information within a
URI. This class allows developers to access information such as the
scheme, path, and hostname. This is great for passing a URI to Web
clients such as the System.Windows.Forms.WebBrowser control or the
System.Net.WebClient class. A companion to the System.Uri class is the
System.UriBuilder class. This class provides a way to modify the
System.Uri class without creating another System.Uri instance. These
classes are the foundation for working with URIs based on the HTTP
protocol. Additional capabilities are needed to support the REST
architectural style used by developers today.
Table 13.1 showed
that developers embed parameters in URIs as either query string
parameters or as parts of the path. The System.Uri or System.UriBuilder
classes do not allow building and parsing of URIs based on this
approach. Another approach that has been used is to build and parse URIs
based on patterns that specify named tokens. The tokens represent the
parameters that are needed to build URIs using logical substitution.
They also define how parameters can be parsed from URIs. .NET Framework
3.5 introduces a new class called the System.UriTemplate that provides a
consistent way for building and parsing URIs based on patterns. This
class defines a pattern based on named tokens. Tokens are represented in
curly braces within a pattern. For example, the pattern
/finance/info?q={symbol} specifies a stock symbol that is sent as a
query string parameter. Named tokens can also be embedded as a part of
the URI path and are not limited to query string parameters. For
example, the following pattern, /browse/{word}, specifies a parameter
within the URI path. System.Uri instances can be built or parsed based
on these patterns. We will now examine how we can use the
System.UriTemplate class do this.
Building URIs
Listing
13.1 shows two examples of how we can build System.Uri instances based
on System.UriTemplate classes. The first example uses the BindByPosition
method to create a System.Uri instance to retrieve Yahoo! stock quotes.
The second example uses the BindByName method to pass a collection of
name/value pairs to create a System.Uri instance to retrieve Google
stock quotes.
Listing 13.1. Binding Parameters with UriTemplate
using System;using System.Collections.Specialized;
namespace EssentialWCF
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string symbol = "MSFT";
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string symbol = "MSFT";
// BindByPosition Uri YahooStockBaseUri =
new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com");
UriTemplate YahooStockUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/d/quotes?s={symbol}&f=sl1t1d1");
Uri YahooStockUri =
YahooStockUriTemplate.BindByPosition(
YahooStockBaseUri,
symbol);
Console.WriteLine(YahooStockUri.ToString());
new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com");
UriTemplate YahooStockUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/d/quotes?s={symbol}&f=sl1t1d1");
Uri YahooStockUri =
YahooStockUriTemplate.BindByPosition(
YahooStockBaseUri,
symbol);
Console.WriteLine(YahooStockUri.ToString());
// BindByName Uri GoogleStockBaseUri =
new Uri("http://finance.google.com");
UriTemplate GoogleStockUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/finance/info?q={symbol}");
NameValueCollection GoogleParams =
new NameValueCollection();
GoogleParams.Add("symbol", symbol);
Uri GoogleStockUri =
GoogleStockUriTemplate.BindByName(
GoogleStockBaseUri,
GoogleParams);
Console.WriteLine(GoogleStockUri.ToString());
new Uri("http://finance.google.com");
UriTemplate GoogleStockUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/finance/info?q={symbol}");
NameValueCollection GoogleParams =
new NameValueCollection();
GoogleParams.Add("symbol", symbol);
Uri GoogleStockUri =
GoogleStockUriTemplate.BindByName(
GoogleStockBaseUri,
GoogleParams);
Console.WriteLine(GoogleStockUri.ToString());
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}
}
}
Parsing URIs
We just saw how easy it was to create System.Uri
instances based on patterns. Listing 13.2 shows how we can take
existing URIs and parse out parameters. Again we have two examples. The
first example shows how we can parse out parameters based on query
string parameters. The second example shows how we can parse out
parameters based on a path. In both cases, we are able to extract a set
of name/value pairs based on a pattern. We will see in the "Creating
Operations for the Web" section how the UriTemplate can be used to dispatch Web service methods based on URIs.
Listing 13.2. Matching Parameters with UriTemplate
using System;
namespace UriTemplate102
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Uri YahooBaseUri = new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com");
UriTemplate YahooStockTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/d/quotes?s={symbol}");
Uri YahooStockUri =
new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes?s=MSFT&f=spt1d");
UriTemplateMatch match =
YahooStockTemplate.Match(YahooBaseUri, YahooStockUri);
foreach (string key in match.BoundVariables.Keys)
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0}: {1}", key,
match.BoundVariables[key]));
Console.WriteLine();
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Uri YahooBaseUri = new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com");
UriTemplate YahooStockTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/d/quotes?s={symbol}");
Uri YahooStockUri =
new Uri("http://finance.yahoo.com/d/quotes?s=MSFT&f=spt1d");
UriTemplateMatch match =
YahooStockTemplate.Match(YahooBaseUri, YahooStockUri);
foreach (string key in match.BoundVariables.Keys)
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0}: {1}", key,
match.BoundVariables[key]));
Console.WriteLine();
Uri ReferenceDotComBaseUri =
new Uri("http://dictionary.reference.com");
UriTemplate ReferenceDotComTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/browse/{word}");
Uri ReferenceDotComUri =
new Uri("http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/opaque");
match =
ReferenceDotComTemplate.Match(ReferenceDotComBaseUri
ReferenceDotComUri);
new Uri("http://dictionary.reference.com");
UriTemplate ReferenceDotComTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/browse/{word}");
Uri ReferenceDotComUri =
new Uri("http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/opaque");
match =
ReferenceDotComTemplate.Match(ReferenceDotComBaseUri
ReferenceDotComUri);
foreach (string key in match.BoundVariables.Keys)
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0}: {1}", key,
match.BoundVariables[key]));
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("{0}: {1}", key,
match.BoundVariables[key]));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
}
}
}
Creating Operations for the Web
Creating
operations for the Web means that we will want to expose services based
on URIs, encode messages without the overhead of SOAP, pass parameters
using the HTTP protocol, and format data using JSON or POX. WCF provides
the WebHttpBinding binding that supports these capabilities. The
WebHttpBinding binding is constructed using two binding elements. The
first binding element is a new message encoder called
WebMessageEncodingBindingElement. This is a new binding element that
allows for the encoding of messages using either JSON or POX. The second
binding element is a transport binding element based on either the
HttpTransportBindingElement or HttpsTransportBindingElement. These
binding elements enable communication using the HTTP protocol. The
HttpsTransportBindingElement binding element is used to support
transport-level security.
Hosting Using WebHttpBinding
To
examine how to use the WebHttpBinding binding, we will create a simple
Echo Web service. We are going to keep this example simple because we
will expand on how to use this binding later on in this chapter. Listing
13.3 shows the IEchoService interface. This interface defines a service
contract that has a single operation contract called Echo. Notice that
the Echo operation contract is also attributed with the WebGet
attribute. This attribute tells the webHttpBinding binding to expose
this operation over the HTTP protocol using the GET verb.
Listing 13.3. IEchoService Interface
using System;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
[ServiceContract]public interface IEchoService
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet]
string Echo(string echoThis);
}
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet]
string Echo(string echoThis);
}
Listing
13.4 shows the EchoService class that implements the IEchoService
interface. This class implements the Echo operation by taking the
echoThis parameter and returning it to the client.
Listing 13.4. EchoService Class
using System;using System.ServiceModel;
public class EchoService : IEchoService
{ #region IEchoService Members
{ #region IEchoService Members
public string Echo(string echoThis)
{
{
return string.Format("You sent this '{0}'.", echoThis);
}
}
#endregion}
The
last thing needed is to host the EchoService service within IIS.
Listing 13.5 shows the configuration file that allows us to host this
service using the WebHttpBinding binding. The webHttpBinding
configuration element exposes services using the WebHttpBinding binding.
One important point is that the WebHttpBinding binding does not specify
the format to expose services. Instead we need to use an endpoint
behavior to specify the format returned from services exposed with the
WebHttpBinding binding. Two endpoint behaviors can be used:
WebHttpBehavior and WebScriptEnablingBehavior. The
WebScriptEnablingBehavior behavior will be discussed in the section
"Programming the Web with AJAX and JSON" later in this chapter. For now
we will discuss the WebHttpBehavior behavior. The WebHttpBehavior
endpoint behavior is used with the WebHttpBinding to format messages
using either JSON or XML. The default for this behavior is to use XML.
Listing 13.5. EchoService Configuration
<system.serviceModel> <services> <service name="EchoService"> <endpoint address="" behaviorConfiguration="WebBehavior" binding="webHttpBinding" contract="IEchoService"/> </service> </services> <behaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior name="WebBehavior"> <webHttp /> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> </behaviors></system.serviceModel>
Figure
13.1 shows the output from the EchoService service when exposed over
the WebHttpBinding binding. Because we exposed the service using the
WebGet attribute, we can call the service by typing the URI in a
browser. The URI that was used is
http://localhost/SimpleWebService/EchoService.svc/Echo?echoThis=helloworld.
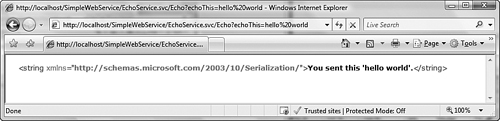
Figure 13.1 Response in browser using WebHttpBinding binding
Using WebGet and WebInvoke
Services
can be exposed using the WebHttpBinding binding using either the WebGet
or WebInvoke attributes. Each of these attributes specifies the HTTP
verb, message format, and body style needed to expose an operation. We
will examine each of these attributes and reasons to use each.
WebGet
The
WebGet attribute exposes operations using the GET verb. The GET has
significant advantages over other HTTP verbs. First, the endpoint is
directly accessible via a Web browser by typing the URI to the service
into the address bar. Parameters can be sent within the URI either as
query string parameters or embedded in the URI. Second, clients and
other downstream systems such as proxy servers can easily cache
resources based on the cache policy for the service. Because of the
caching capability, the WebGet attribute should be used only for
retrieval.
WebInvoke
The
WebInvoke attribute exposes services using other HTTP verbs such as
POST, PUT, and DELETE. The default is to use POST, but it can be changed
by setting the Method property of the attribute. These operations are
meant to modify resources; therefore, the WebInvoke attribute is used to
make modifications to resources.
Listing 13.6 shows a service
that defines services that are exposed in the WebGet and WebInvoke
attributes. The WebGet attribute is used to retrieve customer
information. The WebInvoke attribute is used for those operations that
modify data such as adding or deleting customers. Last, the UriTemplate
property is specified on WebGet and WebInvoke attribute to identify a
customer resource using the URI.
Listing 13.6. CustomerService
using System;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
namespace EssentialWCF
{
[ServiceContract]
public class CustomerService
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public Customer GetCustomer(int id)
{
Customer customer = null;
{
[ServiceContract]
public class CustomerService
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public Customer GetCustomer(int id)
{
Customer customer = null;
// Get customer from database
return customer;
}
}
[OperationContract]
[WebInvoke(Method = "PUT", UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public void PutCustomer(int id, Customer customer)
{
// Put customer in database }
[OperationContract]
[WebInvoke(Method = "DELETE", UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public void DeleteCustomer(int id)
{
// Put customer in database }
}
}
[WebInvoke(Method = "PUT", UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public void PutCustomer(int id, Customer customer)
{
// Put customer in database }
[OperationContract]
[WebInvoke(Method = "DELETE", UriTemplate = "/customer/{id}")]
public void DeleteCustomer(int id)
{
// Put customer in database }
}
}
Programming the Web with AJAX and JSON
So
far we have seen how to host services using the WebHttpBinding binding
and the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior. This allows us to expose
services using POX. Many Web developers want to forgo the use of XML and
instead use JSON, a simpler format. JSON is well suited for browser
applications that need an efficient means of parsing responses from
services, and it has the added benefit of integration with JavaScript,
the programming language most often used for client-side Web
development. JSON is a subset of JavaScript's object literal notation,
which means you can easily create objects in JavaScript. Because of
this, it's a perfect alternative to using XML for use with AJAX
applications.
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
AJAX-based Web applications have significant benefits over traditional
Web applications. They allow for improved user experience and better
bandwidth usage. This is done by improving browser-to-server
communication so that the browser does not need to perform a page load.
This in turn is done by communicating with a server asynchronously using
the JavaScript and the XMLHttpRequest class. Because communication with
the server can be done without the need for a page load, developers can
create richer user interface experiences approaching that of desktop
applications. These types of Web applications are often referred to as
Rich Internet Applications, or RIAs.ASP.NET AJAX Integration
Many
frameworks exist for building these AJAX-based Web applications. One of
the more popular frameworks is the ASP.NET AJAX framework. This
framework has a great client-side and server-side model for building
AJAX-enabled Web applications. It includes many capabilities such as a
rich client-side class library, rich AJAX-enabled Web controls, and
automatic client-side proxy generation for communication with services.
It is also based on ASP.NET, which is Microsoft's technology for
building Web applications using .NET. WCF already integrates with
ASP.NET in .NET Framework 3.0. .NET Framework 3.5 introduces new support
for ASP.NET AJAX applications using the WebScriptEnablingBehavior
endpoint behavior. This replaces the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior.
It adds support for using JSON by default and ASP.NET client-side proxy
generation. These new capabilities can be used by replacing the webHttp
endpoint behavior configuration element with the enableWebScript
configuration element.
We
created a sample ASP.NET AJAX application called the XBOX 360 Game
Review to see how we can use the WebHttpBinding binding and the
WebScriptEnablingBehavior to build AJAX-based applications. This simple
Web application enables users to provide reviews about their favorite
XBOX 360 game. The application was built using an ASP.NET AJAX Web site
project template in Visual Studio 2008. Figure 13.2 shows a picture of
this Web site.
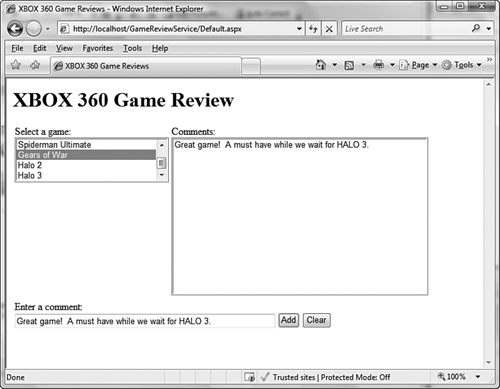
Figure 13.2 XBOX 360 Game Review AJAX-enabled application
This
site has a number of features. First is a list of games that is
displayed in a ListBox control to the user. Users can select a game and
see a list of comments for each game. Then a user can add comments for
the each game. Listing 13.7 lists the service that provides this
functionality.
Listing 13.7. GameReviewService.cs
using System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Runtime.Serialization;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Activation;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
namespace EssentialWCF
{
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "EssentialWCF")]
[ServiceBehavior(InstanceContextMode = InstanceContextMode.Single)]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
public class GameReviewService
{
private string[] gamelist = new string[] { "Viva Pinata",
"Star Wars Lego", "Spiderman Ultimate",
"Gears of War", "Halo 2", "Halo 3" };
private Dictionary<string, List<string>> reviews;
{
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "EssentialWCF")]
[ServiceBehavior(InstanceContextMode = InstanceContextMode.Single)]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Allowed)]
public class GameReviewService
{
private string[] gamelist = new string[] { "Viva Pinata",
"Star Wars Lego", "Spiderman Ultimate",
"Gears of War", "Halo 2", "Halo 3" };
private Dictionary<string, List<string>> reviews;
public GameReviewService()
{
reviews = new Dictionary<string, List<string>>();
foreach (string game in gamelist)
reviews.Add(game, new List<string>());
}
{
reviews = new Dictionary<string, List<string>>();
foreach (string game in gamelist)
reviews.Add(game, new List<string>());
}
[OperationContract]
[WebGet]
public string[] Games()
{
return gamelist;
}
[WebGet]
public string[] Games()
{
return gamelist;
}
[OperationContract]
[WebGet]
public string[] Reviews(string game)
{
WebOperationContext ctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
ctx.OutgoingResponse.Headers.Add("Cache-Control",
"no-cache");
[WebGet]
public string[] Reviews(string game)
{
WebOperationContext ctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
ctx.OutgoingResponse.Headers.Add("Cache-Control",
"no-cache");
if (!reviews.ContainsKey(game))
return null;
return null;
List<string> listOfReviews = reviews[game];
if (listOfReviews.Count == 0)
return new string[] {
string.Format("No reviews found for {0}.",game) };
else return listOfReviews.ToArray();
}
return new string[] {
string.Format("No reviews found for {0}.",game) };
else return listOfReviews.ToArray();
}
[OperationContract]
[WebInvoke]
public void AddReview(string game, string comment)
{
reviews[game].Add(comment);
}
[WebInvoke]
public void AddReview(string game, string comment)
{
reviews[game].Add(comment);
}
[OperationContract]
[WebInvoke]
public void ClearReviews(string game)
{
reviews[game].Clear();
}
}
}
[WebInvoke]
public void ClearReviews(string game)
{
reviews[game].Clear();
}
}
}
We
chose to host this service within Internet Information Server (IIS).
Listing 13.8 shows the GameReviewService.svc used to host the service.
Listing 13.8. GameReviewService.svc
<%@ ServiceHost Language="C#" Debug="true"Service="EssentialWCF.GameReviewService"CodeBehind="~/App_Code/GameReviewService.cs" %>
Listing
13.9 shows the configuration information used to host the
GameReviewService. The most important aspect of this configuration
information is the use of the webHttpBinding binding and the
enableWebScript endpoint behavior. This enables the use of JSON and
generates the necessary client-side proxy code for the GameReviewService
with ASP.NET.
Listing 13.9. web.config
<system.serviceModel> <serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true"/> <services> <service name="EssentialWCF.GameReviewService" behaviorConfiguration="MetadataBehavior"> <endpoint address="" behaviorConfiguration="AjaxBehavior" binding="webHttpBinding" contract="EssentialWCF.GameReviewService"/> <endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding" contract="IMetadataExchange"/> </service> </services> <behaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior name="AjaxBehavior"> <enableWebScript/> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior name="MetadataBehavior"> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" httpGetUrl=""/> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> </behaviors></system.serviceModel>
You
configure the GameReviewService to be used with ASP.NET by adding a
reference to the service using the ASP.NET ScriptManager. Listing 13.10
shows the markup used to reference the GameReviewService. Behind the
scenes this is generating client-side script that references a
JavaScript file with the client-side proxy. For our example, the URI to
the client-side JavaScript is
http://localhost/GameReviewService/GameReviewService.svc/js.
Listing 13.10. Referencing Services Using ASP.NET ScriptManager
<asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server"> <Services> <asp:ServiceReference Path="GameReviewService.svc" /> </Services></asp:ScriptManager>
We
have included the ASP.NET Web form used to build the XBOX 360 Game
Review Web application. This shows how the services are called from
client-side script and how the results are used to dynamically populate
controls.
Listing 13.11. Making Client-Side Proxy Calls
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true"CodeFile="Default.aspx.cs" Inherits="_Default" %>
<%@ Register Assembly="AjaxControlToolkit"Namespace="AjaxControlToolkit" TagPrefix="cc1" %><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN""http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"><head id="Head1" runat="server"> <title>XBOX 360 Game Reviews</title>
<%@ Register Assembly="AjaxControlToolkit"Namespace="AjaxControlToolkit" TagPrefix="cc1" %><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN""http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"><head id="Head1" runat="server"> <title>XBOX 360 Game Reviews</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
function pageLoad() {
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body> <form id="form1" runat="server"> <div> <asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server"> <Services> <asp:ServiceReference Path="GameReviewService.svc" /> </Services> </asp:ScriptManager>
<body> <form id="form1" runat="server"> <div> <asp:ScriptManager ID="ScriptManager1" runat="server"> <Services> <asp:ServiceReference Path="GameReviewService.svc" /> </Services> </asp:ScriptManager>
<script type="text/javascript"> EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.set_defaultFailedCallback(OnError);
function ListGames()
{
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.Games(OnListGamesComplete);
}
function ListReviews()
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.Reviews(gameListBox.value,
OnListReviewsComplete);
}
function AddReview()
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
var reviewTextBox =
document.getElementById("ReviewTextBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.AddReview(gameListBox.value,
reviewTextBox.value, OnUpdateReviews);
}
function ListGames()
{
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.Games(OnListGamesComplete);
}
function ListReviews()
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.Reviews(gameListBox.value,
OnListReviewsComplete);
}
function AddReview()
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
var reviewTextBox =
document.getElementById("ReviewTextBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.AddReview(gameListBox.value,
reviewTextBox.value, OnUpdateReviews);
}
function ClearReviews()
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.ClearReviews(gameListBox.value,
OnUpdateReviews);
}
function OnListGamesComplete(result)
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
ClearAndSetListBoxItems(gameListBox, result);
}
function OnListReviewsComplete(result)
{
var reviewListBox = document.getElementById("ReviewListBox");
ClearAndSetListBoxItems(reviewListBox, result);
}
function OnUpdateReviews(result)
{
ListReviews();
}
function ClearAndSetListBoxItems(listBox, games)
{
for (var i = listBox.options.length-1; i >-1; i--)
{
listBox.options[i] = null;
}
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
EssentialWCF.GameReviewService.ClearReviews(gameListBox.value,
OnUpdateReviews);
}
function OnListGamesComplete(result)
{
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
ClearAndSetListBoxItems(gameListBox, result);
}
function OnListReviewsComplete(result)
{
var reviewListBox = document.getElementById("ReviewListBox");
ClearAndSetListBoxItems(reviewListBox, result);
}
function OnUpdateReviews(result)
{
ListReviews();
}
function ClearAndSetListBoxItems(listBox, games)
{
for (var i = listBox.options.length-1; i >-1; i--)
{
listBox.options[i] = null;
}
var textValue;
var optionItem;
for (var j = 0; j < games.length; j++)
{
var optionItem;
for (var j = 0; j < games.length; j++)
{
textValue = games[j];
optionItem = new Option( textValue, textValue,
false, false);
listBox.options[listBox.length] = optionItem;
}
}
function OnError(result)
{
alert("Error: " + result.get_message());
}
function OnLoad()
{
ListGames();
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
if (gameListBox.attachEvent) {
gameListBox.attachEvent("onchange", ListReviews);
}
else {
gameListBox.addEventListener("change", ListReviews, false);
}
}
Sys.Application.add_load(OnLoad);
</script>
optionItem = new Option( textValue, textValue,
false, false);
listBox.options[listBox.length] = optionItem;
}
}
function OnError(result)
{
alert("Error: " + result.get_message());
}
function OnLoad()
{
ListGames();
var gameListBox = document.getElementById("GameListBox");
if (gameListBox.attachEvent) {
gameListBox.attachEvent("onchange", ListReviews);
}
else {
gameListBox.addEventListener("change", ListReviews, false);
}
}
Sys.Application.add_load(OnLoad);
</script>
<h1>XBOX 360 Game Review</h1> <table> <tr style="height:250px;vertical-align:top"><td style="width:240px">Select a game:<br /><asp:ListBox ID="GameListBox" runat="server" Width="100%"></asp:ListBox></td> <td style="width:400px">Comments:<br /><asp:ListBox ID="ReviewListBox" runat="server" Width="100%" Height="100%"></asp:ListBox></td></tr> <tr style="vertical-align:top"><td colspan="2"> Enter a comment:<br /> <asp:TextBox ID="ReviewTextBox" runat="server" width="400px"></asp:TextBox> <input id="AddReviewButton" type="button" value="Add" onclick="AddReview()" /> <input id="ClearReviewButton" type="button" value="Clear" onclick="ClearReviews()" /> </td></tr> </table> </div> </form></body>
</html>
</html>
Using the WebOperationContext
One
common thing to do when hosting services using the WebHttpBinding
binding is to read or write to the HTTP context. This can be done using
the WebOperationContext class. There are a variety of reasons to access
the HTTP context. You might want to read custom authentication or
authorization headers, control caching, or set the content type, for
example.
Figure 13.3 shows a Web application that displays wallpaper images on the current machine. The entire application is built using a WCF service and is accessible using any Web browser.
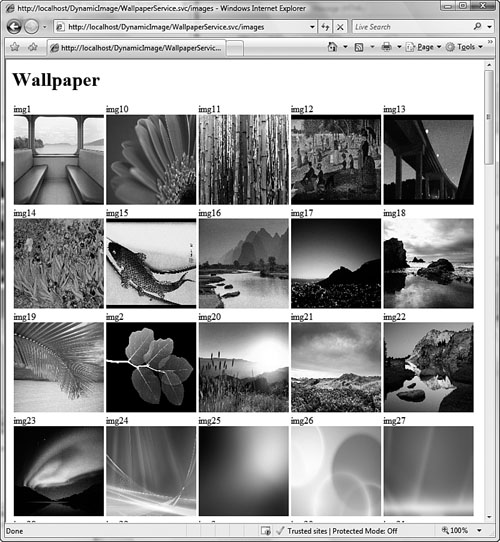
Figure 13.3 Wallpaper Web application
Listing
13.12 shows code for the WallpaperService service. There is an Images
operation that displays an HTML page of all images. This operation sets
the ContentType header so that the browser interprets the output as
HTML. It also sets the Cache-Control header so that additional images
can be added to the application without the browser caching the display.
Finally, there is an Image operation that returns an image to the
browser. This operation sets both the ContentType and ETag header.
Listing
13.17 shows the code to host the syndication service. The application
self-hosts the service using the WebServiceHost class. It then consumes
the service and outputs the feed to the display.
Figure 13.3 shows a Web application that displays wallpaper images on the current machine. The entire application is built using a WCF service and is accessible using any Web browser.

Figure 13.3 Wallpaper Web application
Listing 13.12. Wallpaper Image Service
using System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.IO;using System.Runtime.Serialization;using System.Text;using System.Web.UI;using System.Web.UI.WebControls;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Activation;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
namespace EssentialWCF
{
[DataContract]
public class Image {
string name;
string uri;
{
[DataContract]
public class Image {
string name;
string uri;
public Image()
{
}
{
}
public Image(string name, string uri)
{
this.name = name;
this.uri = uri;
}
{
this.name = name;
this.uri = uri;
}
public Image(string name, Uri uri)
{
this.name = name;
this.uri = uri.ToString();
}
{
this.name = name;
this.uri = uri.ToString();
}
[DataMember]
public string Name
{
get { return this.name; }
set { this.Name = value; }
}
[DataMember]
public string Uri
{
get { return this.uri; }
set { this.uri = value; }
}
}
public string Name
{
get { return this.name; }
set { this.Name = value; }
}
[DataMember]
public string Uri
{
get { return this.uri; }
set { this.uri = value; }
}
}
[ServiceContract]
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Required)]
public class WallpaperService {
private static UriTemplate ImageUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/image/{name}");
private string ImagePath
{
get {
return @"C:\Windows\Web\Wallpaper";
}
}
[AspNetCompatibilityRequirements(RequirementsMode =
AspNetCompatibilityRequirementsMode.Required)]
public class WallpaperService {
private static UriTemplate ImageUriTemplate =
new UriTemplate("/image/{name}");
private string ImagePath
{
get {
return @"C:\Windows\Web\Wallpaper";
}
}
private Image GetImage(string name, Uri baseUri)
{
return new Image(name,
ImageUriTemplate.BindByPosition(baseUri,
new string[] { name }));
}
{
return new Image(name,
ImageUriTemplate.BindByPosition(baseUri,
new string[] { name }));
}
private void PopulateListOfImages(List<Image> list,
Uri baseUri)
{
System.Web.HttpContext ctx =
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
DirectoryInfo d = new DirectoryInfo(ImagePath);
FileInfo[] files = d.GetFiles("*.jpg");
Uri baseUri)
{
System.Web.HttpContext ctx =
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
DirectoryInfo d = new DirectoryInfo(ImagePath);
FileInfo[] files = d.GetFiles("*.jpg");
foreach (FileInfo f in files)
{
string fileName = f.Name.Split(new char[] { '.' })[0];
string etag = fileName + "_" +
f.LastWriteTime.ToString();
list.Add(GetImage(fileName, baseUri));
}
}
{
string fileName = f.Name.Split(new char[] { '.' })[0];
string etag = fileName + "_" +
f.LastWriteTime.ToString();
list.Add(GetImage(fileName, baseUri));
}
}
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/images")]
public void Images()
{
WebOperationContext wctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
wctx.OutgoingResponse.ContentType = "text/html";
wctx.OutgoingResponse.Headers.Add("Cache-Control",
"no-cache");
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/images")]
public void Images()
{
WebOperationContext wctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
wctx.OutgoingResponse.ContentType = "text/html";
wctx.OutgoingResponse.Headers.Add("Cache-Control",
"no-cache");
Uri baseUri =
wctx.IncomingRequest.UriTemplateMatch.BaseUri;
List<Image> listOfImages = new List<Image>();
PopulateListOfImages(listOfImages, baseUri);
wctx.IncomingRequest.UriTemplateMatch.BaseUri;
List<Image> listOfImages = new List<Image>();
PopulateListOfImages(listOfImages, baseUri);
TextWriter sw = new StringWriter();
Html32TextWriter htmlWriter = new Html32TextWriter(sw);
Html32TextWriter htmlWriter = new Html32TextWriter(sw);
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("HTML");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("BODY");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("H1");
htmlWriter.Write("Wallpaper");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("H1");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TABLE");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TR");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("BODY");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("H1");
htmlWriter.Write("Wallpaper");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("H1");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TABLE");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TR");
int i = 0;
Image image;
while (i < listOfImages.Count)
{
image = listOfImages[i];
Image image;
while (i < listOfImages.Count)
{
image = listOfImages[i];
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TD");
htmlWriter.Write(image.Name);
htmlWriter.WriteBreak();
htmlWriter.WriteBeginTag("IMG");
htmlWriter.WriteAttribute("SRC", image.Uri);
htmlWriter.WriteAttribute("STYLE",
"width:150px;height:150px");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("IMG");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TD");
htmlWriter.Write(image.Name);
htmlWriter.WriteBreak();
htmlWriter.WriteBeginTag("IMG");
htmlWriter.WriteAttribute("SRC", image.Uri);
htmlWriter.WriteAttribute("STYLE",
"width:150px;height:150px");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("IMG");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TD");
if (((i + 1) % 5) == 0)
{
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TR");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TR");
}
i++;
}
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TR");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TABLE");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("BODY");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("HTML");
{
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TR");
htmlWriter.WriteFullBeginTag("TR");
}
i++;
}
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TR");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("TABLE");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("BODY");
htmlWriter.WriteEndTag("HTML");
System.Web.HttpContext ctx =
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
ctx.Response.Write(sw.ToString());
}
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
ctx.Response.Write(sw.ToString());
}
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/image/{name}")]
public void GetImage(string name)
{
WebOperationContext wctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
wctx.OutgoingResponse.ContentType = "image/jpeg";
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/image/{name}")]
public void GetImage(string name)
{
WebOperationContext wctx = WebOperationContext.Current;
wctx.OutgoingResponse.ContentType = "image/jpeg";
System.Web.HttpContext ctx =
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
string fileName = null;
byte[] fileBytes = null;
try {
fileName = string.Format(@"{0}\{1}.jpg",
ImagePath,
name);
if (File.Exists(fileName))
{
using (FileStream f = File.OpenRead(fileName))
{
fileBytes = new byte[f.Length];
f.Read(fileBytes, 0,Convert.ToInt32(f.Length));
}
}
else wctx.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode =
System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
}
catch {
wctx.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode =
System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
}
System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
string fileName = null;
byte[] fileBytes = null;
try {
fileName = string.Format(@"{0}\{1}.jpg",
ImagePath,
name);
if (File.Exists(fileName))
{
using (FileStream f = File.OpenRead(fileName))
{
fileBytes = new byte[f.Length];
f.Read(fileBytes, 0,Convert.ToInt32(f.Length));
}
}
else wctx.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode =
System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
}
catch {
wctx.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode =
System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
}
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(fileName);
wctx.OutgoingResponse.ETag = fileName + "_" +
fi.LastWriteTime.ToString();
ctx.Response.OutputStream.Write(fileBytes, 0,
fileBytes.Length);
}
}
}
The
following configuration in Listing 13.13 is used to host the
WallpaperService service. The service is hosted using the WebHttpBinding
binding and the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior.wctx.OutgoingResponse.ETag = fileName + "_" +
fi.LastWriteTime.ToString();
ctx.Response.OutputStream.Write(fileBytes, 0,
fileBytes.Length);
}
}
}
Listing 13.13. Wallpaper Image Service Configuration
<system.serviceModel> <serviceHostingEnvironment aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true"/> <services> <service name="EssentialWCF.WallpaperService" behaviorConfiguration="MetadataBehavior"> <endpoint address="" behaviorConfiguration="WebBehavior" binding="webHttpBinding" contract="EssentialWCF.WallpaperService"/> <endpoint address="mex" binding="mexHttpBinding" contract="IMetadataExchange"/> </service> </services> <behaviors> <endpointBehaviors> <behavior name="WebBehavior"> <webHttp /> </behavior> </endpointBehaviors> <serviceBehaviors> <behavior name="MetadataBehavior"> <serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" httpGetUrl="" /> </behavior> </serviceBehaviors> </behaviors></system.serviceModel>
Listing 13.14 shows the .svc file used to host the WallpaperService in IIS.Listing 13.14. WallpaperService.svc
<%@ ServiceHost Language="C#" Debug="true"Service="EssentialWCF.WallpaperService"CodeBehind="~/App_Code/WallpaperService.cs" %>
Hosting for the Web
Arguably
one of the best improvements in WCF is the feature for hosting services
on the Web. Prior to .NET Framework 3.5, you had to provide
configuration or write code to host services. This was true even if you
hosted your services within IIS. This became tedious for those hosting
services on the Web. There are many capabilities offered by WCF to host
services, but only a limited configuration was used by Web developers
building services. For example, you would not expect an AJAX-based
application to support multiple bindings, use message-level security, or
require transactions. To simplify hosting of services, WCF introduced a
feature called Configuration Free Hosting. This allows developers to
host services without providing configuration or writing any code. The
infrastructure for this feature was always a part of the hosting model
within WCF. We will examine two ways to use this feature.
WebScriptServiceHost
There
is a new class available in the System.ServiceModel.Web namespace
called the WebScriptServiceHost class. This class allows for
self-hosting of services using the WebHttpBinding binding and the
WebScriptEnablingBehavior endpoint behavior. The advantage to using this
class over the ServiceHost class is that you do not have to provide any
binding or behaviors to host a service.
WebScriptServiceHostFactory
Another
class in the System.ServiceModel.Activation namespace, called the
WebScriptServiceHostFactory class, is meant to be used with IIS hosting
and .svc files. It allows for hosting of services in IIS using the
WebHttpBinding binding and the WebScriptEnablingBehavior endpoint
behavior without the need for configuration. Listing 13.15 shows an
example of an .svc file that uses the WebScriptServiceHostFactory class.
This is the same .svc file used to host the WallpaperService service
shown in Listing 13.12. The advantage of this approach is that the
configuration information shown in Listing 13.13 is no longer required
to host the service.
NOTE: Configuration-Free Hosting for WebHttp
Two additional classes, called WebServiceHost and WebServiceHostFactory, host services using the WebHttpBinding binding and the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior. They offer the same configuration-free hosting capabilities as the WebScriptServiceHost and WebScriptServiceHostFactory classes.
NOTE: Configuration-Free Hosting for WebHttp
Two additional classes, called WebServiceHost and WebServiceHostFactory, host services using the WebHttpBinding binding and the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior. They offer the same configuration-free hosting capabilities as the WebScriptServiceHost and WebScriptServiceHostFactory classes.
Listing 13.15. WallpaperService.svc (Configuration Free)
<%@ ServiceHost Factory="System.ServiceModel.Activation.WebScriptServiceHostFactory"Language="C#" Debug="true" Service="EssentialWCF.WallpaperService"CodeBehind="~/App_Code/WallpaperService.cs" %>
Content Syndication with RSS and ATOM
RSS and ATOM are content syndication formats for the Web. These formats are used for all types of content syndication, such as news, video, and blogs. By far the widest use for these formats is for blogging. Since its initial popularity, RSS and ATOM have been used by every major Web site. WCF provides several mechanisms for working with RSS and ATOM syndication feeds. A new namespace, called System.ServiceModel.Syndication, contains classes for creating, consuming, and formatting syndication feeds based on RSS and ATOM. The core class for creating and consuming content syndication feeds is the SyndicationFeed class. Listing 13.16 shows an example application using this class to expose an RSS and ATOM. This application enumerates over a music collection and exposes the information using a syndication feed.Listing 13.16. Zune Music Syndication
using System;using System.IO;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Syndication;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
[ServiceContract]public class ZuneFeedService
{
private static Uri LiveSearchBaseURI =
new Uri("http://search.live.com");
private static UriTemplate LiveSearchTemplate =
new UriTemplate(@"/results.aspx?q={terms}");
[ServiceContract]public class ZuneFeedService
{
private static Uri LiveSearchBaseURI =
new Uri("http://search.live.com");
private static UriTemplate LiveSearchTemplate =
new UriTemplate(@"/results.aspx?q={terms}");
private string MusicPath
{
get {
return @"C:\Users\ricrane\Music\Zune";
}
}
{
get {
return @"C:\Users\ricrane\Music\Zune";
}
}
private SyndicationFeed ZuneFeed
{
get {
SyndicationFeed feed = new SyndicationFeed()
{
Title =
new TextSyndicationContent("My Zune Music Library"),
Description =
new TextSyndicationContent("My Zune Music Library")
};
{
get {
SyndicationFeed feed = new SyndicationFeed()
{
Title =
new TextSyndicationContent("My Zune Music Library"),
Description =
new TextSyndicationContent("My Zune Music Library")
};
DirectoryInfo di = new DirectoryInfo(MusicPath);
DirectoryInfo[] artists = di.GetDirectories();
DirectoryInfo[] artists = di.GetDirectories();
List<SyndicationItem> items = new List<SyndicationItem>();
foreach (DirectoryInfo artist in artists)
{
SyndicationItem item = new SyndicationItem()
{
Title =new TextSyndicationContent(string.Format("Artist: {0}", artist.Name)),
Summary =
new TextSyndicationContent(artist.FullName),
PublishDate = DateTime.Now,
LastUpdatedTime = artist.LastAccessTime,
Copyright =
new TextSyndicationContent(@"Zune Library (c)")
};
Uri searchUri =
LiveSearchTemplate.BindByPosition(LiveSearchBaseURI, artist.Name);
item.Links.Add(new SyndicationLink(searchUri));
items.Add(item);
}
foreach (DirectoryInfo artist in artists)
{
SyndicationItem item = new SyndicationItem()
{
Title =new TextSyndicationContent(string.Format("Artist: {0}", artist.Name)),
Summary =
new TextSyndicationContent(artist.FullName),
PublishDate = DateTime.Now,
LastUpdatedTime = artist.LastAccessTime,
Copyright =
new TextSyndicationContent(@"Zune Library (c)")
};
Uri searchUri =
LiveSearchTemplate.BindByPosition(LiveSearchBaseURI, artist.Name);
item.Links.Add(new SyndicationLink(searchUri));
items.Add(item);
}
feed.Items = items;
return feed;
}
}
}
}
[OperationContract]
[WebGet]
[ServiceKnownType(typeof(Atom10FeedFormatter))]
[ServiceKnownType(typeof(Rss20FeedFormatter))]
public SyndicationFeedFormatter<SyndicationFeed>
GetMusic(string format)
{
SyndicationFeedFormatter<SyndicationFeed> output;
[WebGet]
[ServiceKnownType(typeof(Atom10FeedFormatter))]
[ServiceKnownType(typeof(Rss20FeedFormatter))]
public SyndicationFeedFormatter<SyndicationFeed>
GetMusic(string format)
{
SyndicationFeedFormatter<SyndicationFeed> output;
if (format == "rss")
output = new Rss20FeedFormatter(ZuneFeed);
else output = new Atom10FeedFormatter(ZuneFeed);
output = new Rss20FeedFormatter(ZuneFeed);
else output = new Atom10FeedFormatter(ZuneFeed);
return output;
}
}
}
}
Listing
13.17 shows the code to host the syndication service. The application
self-hosts the service using the WebServiceHost class. It then consumes
the service and outputs the feed to the display.
Listing 13.17. Zune Music Feed Console Application
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Diagnostics;using System.ServiceModel;using System.ServiceModel.Description;using System.ServiceModel.Syndication;using System.ServiceModel.Web;
namespace ZuneFeed
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(ZuneFeedService),
new Uri("http://localhost:8000/zune"));
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(ZuneFeedService),
new Uri("http://localhost:8000/zune"));
ServiceEndpoint atomEndpoint =
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(ZuneFeedService),
new WebHttpBinding(), "feed");
atomEndpoint.Behaviors.Add(new WebHttpBehavior());
host.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(ZuneFeedService),
new WebHttpBinding(), "feed");
atomEndpoint.Behaviors.Add(new WebHttpBehavior());
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service host open");
SyndicationFeed feed =
SyndicationFeed.Load(
new Uri("http://localhost:8000/zune/feed/?format=rss"));
SyndicationFeed.Load(
new Uri("http://localhost:8000/zune/feed/?format=rss"));
foreach (SyndicationItem item in feed.Items)
{
Console.WriteLine("Artist: " + item.Title.Text);
Console.WriteLine("Summary: " + item.Summary.Text);
}
{
Console.WriteLine("Artist: " + item.Title.Text);
Console.WriteLine("Summary: " + item.Summary.Text);
}
Console.WriteLine("Press [Enter] to exit.]");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Summary
The
new Web programming capabilities in WCF simplify the building of
services for use on the Web. They help Web developers get stuff done
quickly in the manner that they wish to build and consume services for
the Web. This means providing features that allow developers to work
with the Web. The following summarizes those capabilities of WCF for the
Web:
- The .NET Framework 3.5 provides a new UriTemplate class that allows for the efficient parsing of URIs based on their path and a query component. The UriTemplate class is used by WCF in its Web programming model calls to services.
- Information can be exposed with WCF using a variety of serialization formats including SOAP and POX. .NET Framework 3.5 adds support for JSON as a serialization format.
- An additional binding provided by WCF, called the webHttpBinding binding, exposes services using WCF's Web programming model.
- The webHttpBinding binding is used with either the WebHttpBehavior or WebScriptEnablingBehavior endpoint behaviors. The WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior is used to expose services using POX or JSON. The WebScriptEnablingBehavior endpoint behavior is using JSON with additional support for generating ASP.NET AJAX client proxies.
- WCF provides a new hosting feature called configuration-free hosting. This feature allows services to be hosted in IIS without the need for configuration. Out of the box, WCF provides two classes that support configuration-free hosting: WebServiceHostFactory and WebScriptServiceHostFactory. The WebServiceHostFactory supports configuration-free hosting using the webHttpBinding binding and the WebHttpBehavior endpoint behavior. The WebScriptServiceHostFactory supports configuration-free hosting using the webHttpBinding binding and the WebScriptEnablingBehavior endpoint behavior.
- WCF in .NET Framework 3.5 provides a rich extensible programming model for content syndication found in the System.ServiceModel.Syndication namespace. Support for both RSS and ATOM syndication feeds is included, using the Atom10FeedFormatter and Rss20FeedFormatter classes.
No comments:
Post a Comment